What is SVM?
A Support Vector Machine is a learning algorithm typically used for classification
problems (Weather prediction, text categorization, handwritten character recognition, image
classification,Facial expression classification etc.). ie, if we have some sets of things classified
But we know nothing about how we classified it, or we don't know the rules used for classification),
when a new data comes, SVM can PREDICT which set the data should belong to.
Suppose we have to differentiate a square from rectangle. how can we do it?
we know the logic is
if length=breadth then it is a square
else
it is a rectangle.
this is the logic we want to cluster using the SVM, we would have to give the have data in following format:
1 1:2 2:2
1 1:4 2:4
1 1:9 2:9
1 1:10 2:10
..........
..........
-1 1:5 2:6
-1 1:3 2:4
-1 1:6 2:9
-1 1:4 2:1
..........
..........
The above example is a TWO-class classification with labels +1 and -1 . +1 represents square and -1 represents rectangle.
Consider the 4 th line in the above format ie 1 1:10 2:10
1 represents this is a square.
For the second column (eg: 1:10) 1: represents the index value and 10 represents the length.
For the third column (eg: 2:10) 2: represents the index value and 10 represents the bredth.
Consider the 8 th line in the above format ie -1 1:4 2:1
-1 represents this is a rectangle.
For the second column (eg: 1:4) 1: represents the index value and 4 represents the length.
For the third column (eg: 2:1) 2: represents the index value and 1 represents the bredth.
This is the input file format of SVM.
[label] [index1]:[value1] [index2]:[value2] ...
[label] [index1]:[value1] [index2]:[value2] ...
label
Sometimes referred to as 'class', the class (or set) of your classification. Usually we put integers here.
index
Ordered indexes. usually continuous integers.
value
The data for training. Usually lots of real (floating point) numbers.
Why value, value2, ...?
The reason is usually the input data to the problem you were trying to solve involves lots of 'features'
or say 'attributes', so the input will be a set (or say vector/array).
For the above example we have 2 features lenght and breadth.
Installing Libsvm
We can download the libsvm from http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/
libsvm.zip or libsvm.tar.gz
Contents in the .zip and .tar.gz are the same.
For windows users unzip the file. libsvm folder will be created.
UNIX users mostly prefer .tar.gz.
What is Libsvm?
Libsvm is a library for support vector machines.
How to Use Libsvm
We must follow the below procedure :
1. Data Preparation for SVM
2. Convert data into SVM format
3. Conduct simple scaling on the data
4. Consider the RBF kernel K(x; y) = e
5. Use cross-validation to find the best parameter C and gamma
6. Use the best parameter C and gamma to train the whole training set
7. Test
We discuss this procedure in detail in the following sections
1. Data Preparation for SVM
We need to collect maximum data as possible. data set should contains both positive and negative data.
if it contains only one type of data(ie either positive or negative), it will shows wrong accuracy.
The selection of a negative data set is essential to the reliability of the prediction model.
we need to split the data set into two, one for training and other for testing.
After collecting the data , we need to convert both the training set and testing set into SVM format.
2. Convert the data into SVM format
The SVM algorithm operates on numeric attributes.
So we need to convert the data into libsvm format which contains only numerical values.
For example , If we have imaginary data records like this:
man voice:low figure:big income:good
woman voice:high figure:slim income:fare
1. Convert the feature values to its numeric representation.
Let's say, that best salary would be 5 and worst salary 1 (or no salary = 0), the same with other enumarated variables.
2. We have 2 classes, man and women . convert the classes to numeric values: man = 1, woman = -1
3. Save it in libsvm data format:
[class/target] 1:[firstFeatureValue] 2:[secondFeatureValue] etc.
ex.:
a women with great salary, low voice and small figure would be encoded like:
-1 1:5 2:1.5 3:1.8
In general the input file format of SVM is
[label] [index1]:[value1] [index2]:[value2] ...
[label] [index1]:[value1] [index2]:[value2] ...
label
Sometimes referred to as 'class', the class (or set) of your classification. Usually we put integers here.
index
Ordered indexes. usually continuous integers.
value
The data for training. Usually lots of real (floating point) numbers.
Is there a program to check if my data are in the correct format?
yes.
we can use the python script libsvm-3.11/tools /checkdata.py
Before doing that you need to install Python.
put checkdata.py in the Python folder. open a command prompt and type python checkdata.py filename.
3. Conduct simple scaling on the data
The original data maybe too huge or small in range, thus we can
rescale them to the proper range so that training and predicting will be faster.
The main advantage of scaling is to avoid attributes in greater numeric
ranges dominating those in smaller numeric ranges. Another advantage is to avoid
numerical difficulties during the calculation.
We recommend linearly scaling each attribute to the range [1; +1] or [0; 1].
we have to use the same method to scale both training and testing
data.
svm-scale is a tool for scaling input data file.
It is available at libsvm-3.11\windows
The syntax of svm-scale is
svm-scale [options] data_filename.
For options please refer README file in libsvm.
Running the above command generates 2 files. training.scale and range file.
In the above example we scale the file training.txt and scale each attribute/feature to the range [-1 +1].
The output of scaling is training.scale file, which is used for creating the model.
(model will be discussed later).
here we use option -s for saving the scaling parameters to range file.
Scaling factors are stored in the file range and that file is used for scaling the
test data.
we should scale the testing and scaling data in same range.
so for scaling the testing file we can use the range file .
Above example uses the range file for scaling the testing data. It generates the output testing.scale.
note: we can scale training and testing data in a similar way.
> svm-scale -s scaling_parameters train_data > scaled_train_data
> svm-scale -r scaling_parameters test_data > scaled_test_data
But using the same scaling factors for training and testing sets, we obtain much better
accuracy
4. Model Selection
After scaling the data set , we have to choose a kernel function for creating the model.
4 basic kernels are
- linear
- polynomial
- radial basis function
- sigmoid
In general, the RBF kernel is a reasonable first choice.
A recent result shows that if RBF is used with model selection, then there is no need to consider the linear kernel. The kernel matrix using sigmoid may not be positive definite and in general it's accuracy is not better than RBF. Polynomial kernels are ok but if a high degree is used, numerical difficulties tend to happen.
In some cases RBF kernel is not used.
case 1: Number of instances < number of features/attributes
(instance means each entry in the txt file)
Consider an
example1 .
we have 2 data sets one for training and other for testing
training set contains 38 instance and testing set contains 34 instance. number of features:7,129.
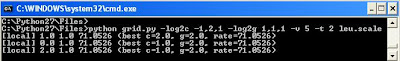
If you use RBF kernel the accuracy is 71.05
and for linear kernel accuracy is 94.73 (please see below)
In such cases linear kernel have more accuracy than RBF kernel.
There are two parameters for an RBF kernel: C and gamma
linear kernel has a penalty parameter C.
It is not known beforehand which C and gamma are best for a given problem; consequently some kind of model selection(parameter search) must be done. The goal is to identify good (C , gamma) so that the
classifier can accurately predict unknown data (i.e. testing data).
For selecting the best parameter value , we can use grid.py in the libsvm-3.11\tools directory.
grid.py is a parameter selection tool for C-SVM classification using
the RBF (radial basis function) kernel. It uses cross validation (CV) (will discuss later)
technique to estimate the accuracy of each parameter combination in
the specified range and helps you to decide the best parameters for
your problem.
grid.py directly executes libsvm binaries (so no python binding is needed)
for cross validation and then draw contour of CV accuracy using gnuplot.
Before using the grid.py , we should edit grid.py for setting the path of svmtrain_exe and gnuplot_exe
grid.py
if not is_win32:
svmtrain_exe = "../svm-train"
gnuplot_exe = "/usr/bin/gnuplot"
else:
# example for windows
svmtrain_exe = r"
F:\lekshmi\libsvm-3.11\windows\svm-train.exe"
# svmtrain_exe = r"c:\Program Files\libsvm\windows\svm-train.exe"
gnuplot_exe = r"
F:\lekshmi\gp444win32\gnuplot\binary\gnuplot.exe"
you should install python and gnuplot before running grid.py.
After installing python set the environment variable "PYTHONPATH" as C:\Python27(in my system python is installed in C directory)
put the grid.py in the python folder. open the command promt and change directory to the folder contains grid.py.
Consider the above example1 (Number of instances < number of features/attributes)
for linear kernel
for RBF kernel
now we can discuss the grid.py in detail
The syntax for grid.py is
grid.py [-log2c begin,end,step] [-log2g begin,end,step] [-v fold]
[-svmtrain pathname] [-gnuplot pathname] [-out pathname] [-png pathname]
[additional parameters for svm-train] dataset